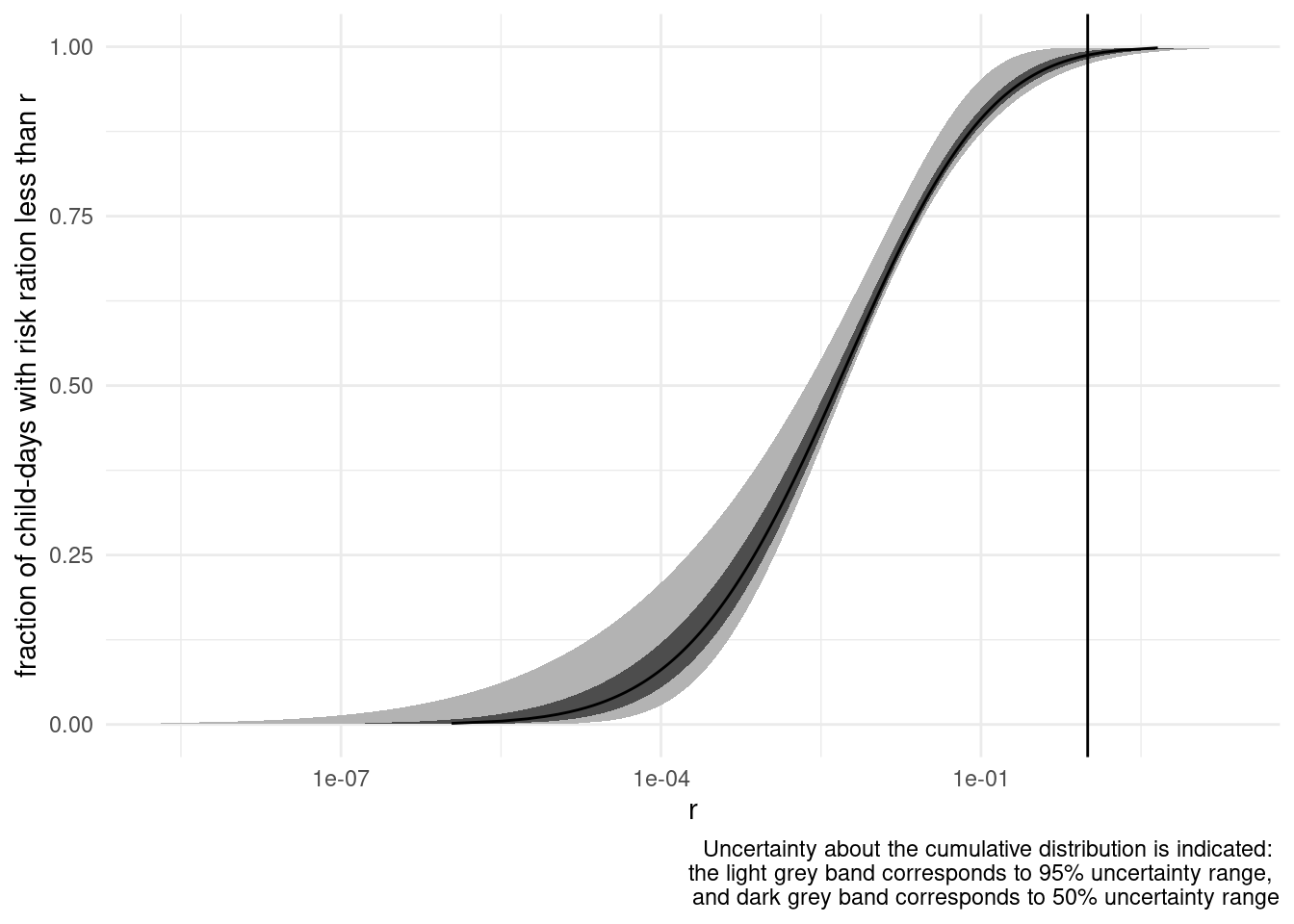
Two-dimensional probability distribution
In the Guidance on Uncertainty, the term ‘two-dimensional (or 2D) probability distribution’ refers to a distribution that quantifies the uncertainty of a quantity that is variable, i.e. takes multiple true values (e.g. the exposure of different individuals in a population).
A 2D probability distribution is most often plotted as a Cumulative Distribution Function (CDF) or Complementary CDF representing the median estimate of the variability, with uncertainty intervals quantifying uncertainty around the CDF or CCDF (Figure 1).
You can learn more about the 2D probability distribution on the page for probability distributions in the section introducing uncertainty and variability.